作者:Ted Lee
本文使用 ChatGPT 來生成圖檔(photo)、影片檔(video)與音檔(audio)三大類常見的多媒體播放器(multimedia player)的 Python 程式碼。
其中,我們在圖檔播放器中餵入「UI(User Interface,使用者界面)設計稿」來指引 ChatGPT 依此版面安排各 Tkinter 的視窗元件(window components)。
此外,在影片檔播放器的程式碼生成過程中,我們將引導讀者 Python 處理在影片檔播放前需要安裝哪些合適的套件(package)/模組(module)。
最後,我們將在 fChart 裝入 pygame 套件來完成音檔的播放功能。
一、圖檔播放器
首先,我們使用自編的網頁教材 ,讓學生們先搜尋這類播放器的 UI 畫面設計。果然,年輕的學生常常是天生的藝術家,我們列舉一些優良的作品如圖 1 所示。
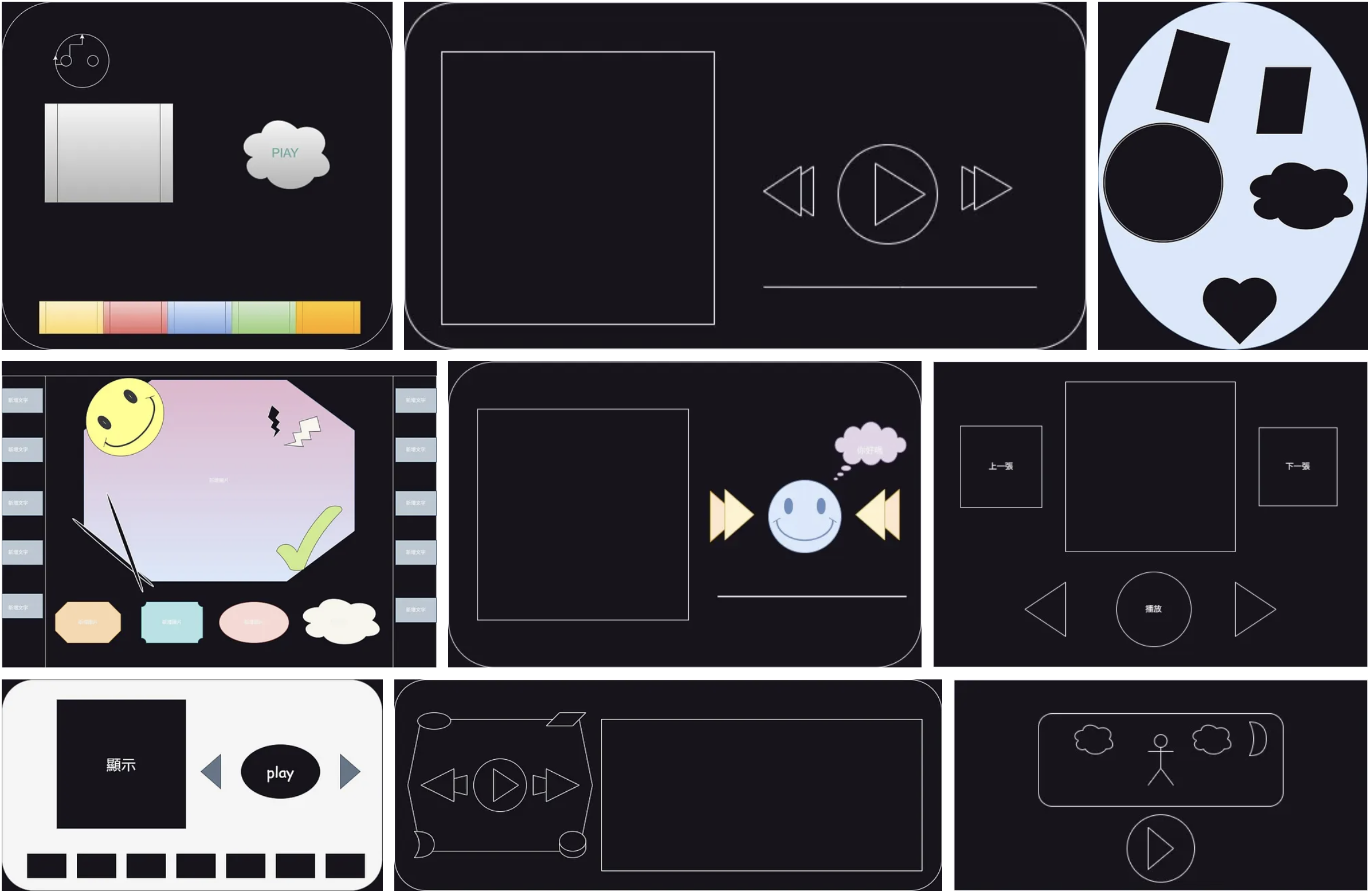
圖 1:學生的 UI 設計稿
接著,我們 在 ChatGPT(其他 GPT 版本亦同)使用以下的咒語:
(人設)你是 Python Tkinter 視窗程式設計高手
(任務)根據「設計稿」,產生圖片播放器,要支援各種常見的圖片格式
(輸出)生成 Python 程式碼
註:生成式 AI 一定有答案,答案不止一套,並且常常胡說八道!
生成的參考程式碼如下:
PhotoPlayer.py
import os
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
# 全域變數
root = None
canvas = None
image_list = []
image_index = 0
tk_image = None
supported_formats = ('.png', '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.bmp', '.gif')
def load_images():
"""載入圖片資料夾"""
global image_list, image_index
folder_path = filedialog.askdirectory(title="選擇圖片資料夾")
if not folder_path:
return
image_list = [
os.path.join(folder_path, f)
for f in os.listdir(folder_path)
if f.lower().endswith(supported_formats)
]
image_list.sort()
image_index = 0
if image_list:
show_image()
def show_image():
"""顯示當前圖片"""
global tk_image
if not image_list:
return
image_path = image_list[image_index]
img = Image.open(image_path)
# 取得視窗大小並等比例縮放圖片
canvas_width = canvas.winfo_width()
canvas_height = canvas.winfo_height()
img.thumbnail((canvas_width, canvas_height))
tk_image = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img)
canvas.delete("all")
canvas.create_image(canvas_width // 2, canvas_height // 2, image=tk_image, anchor=tk.CENTER)
root.title(f"圖片播放器 - {os.path.basename(image_path)}")
def show_next_image():
"""顯示下一張圖片"""
global image_index
if image_list:
image_index = (image_index + 1) % len(image_list)
show_image()
def show_prev_image():
"""顯示上一張圖片"""
global image_index
if image_list:
image_index = (image_index - 1) % len(image_list)
show_image()
def on_resize(event):
"""視窗大小改變時重新顯示圖片"""
show_image()
def create_gui():
"""建立GUI介面"""
global root, canvas
# 建立主視窗
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("圖片播放器")
root.geometry("800x600")
# 建立畫布
canvas = tk.Canvas(root, bg="black")
canvas.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
# 建立控制按鈕框架
control_frame = tk.Frame(root)
control_frame.pack(fill=tk.X, pady=5)
# 建立按鈕
tk.Button(control_frame, text="開啟資料夾", command=load_images).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
tk.Button(control_frame, text="上一張", command=show_prev_image).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
tk.Button(control_frame, text="下一張", command=show_next_image).pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=5)
# 綁定視窗大小改變事件
root.bind("", on_resize)
def main():
"""主程式"""
create_gui()
root.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
以上程式碼在 fChart 的執行畫面如圖 2(測試素材可由此下載):
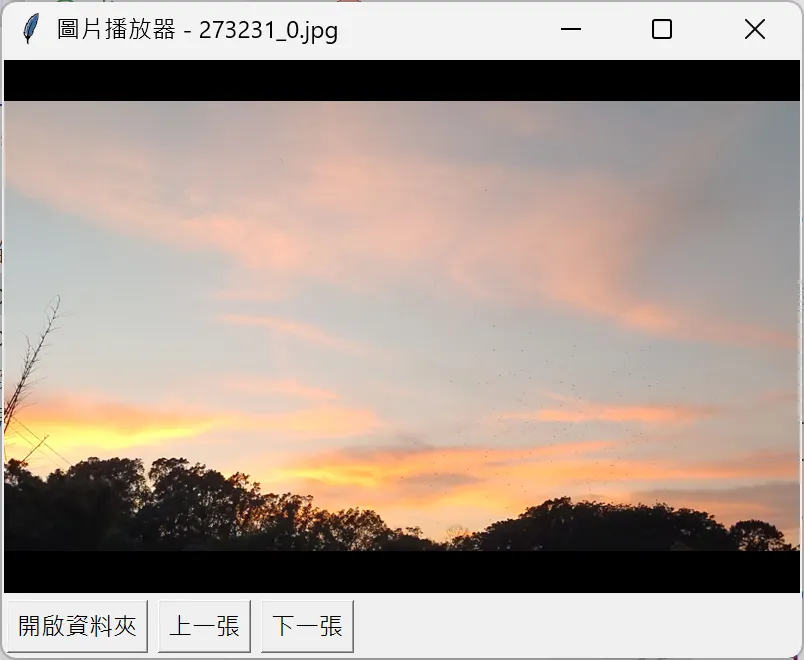
圖 2:PhotoPlayer.py 的執行結果
ChatGPT 果然看不懂學生手繪的設計稿!!!
於是,我們在教學時特地引導學生去思考要如何教 ChatGPT「看懂圖」這回事。註:就用「我們怎們教別人看懂自己的設計稿」的概念,明確標示出稿上每一處的用途!
果不期然,高手在學生。有學生叫 ChatGPT 照稿生出來了(圖 3):
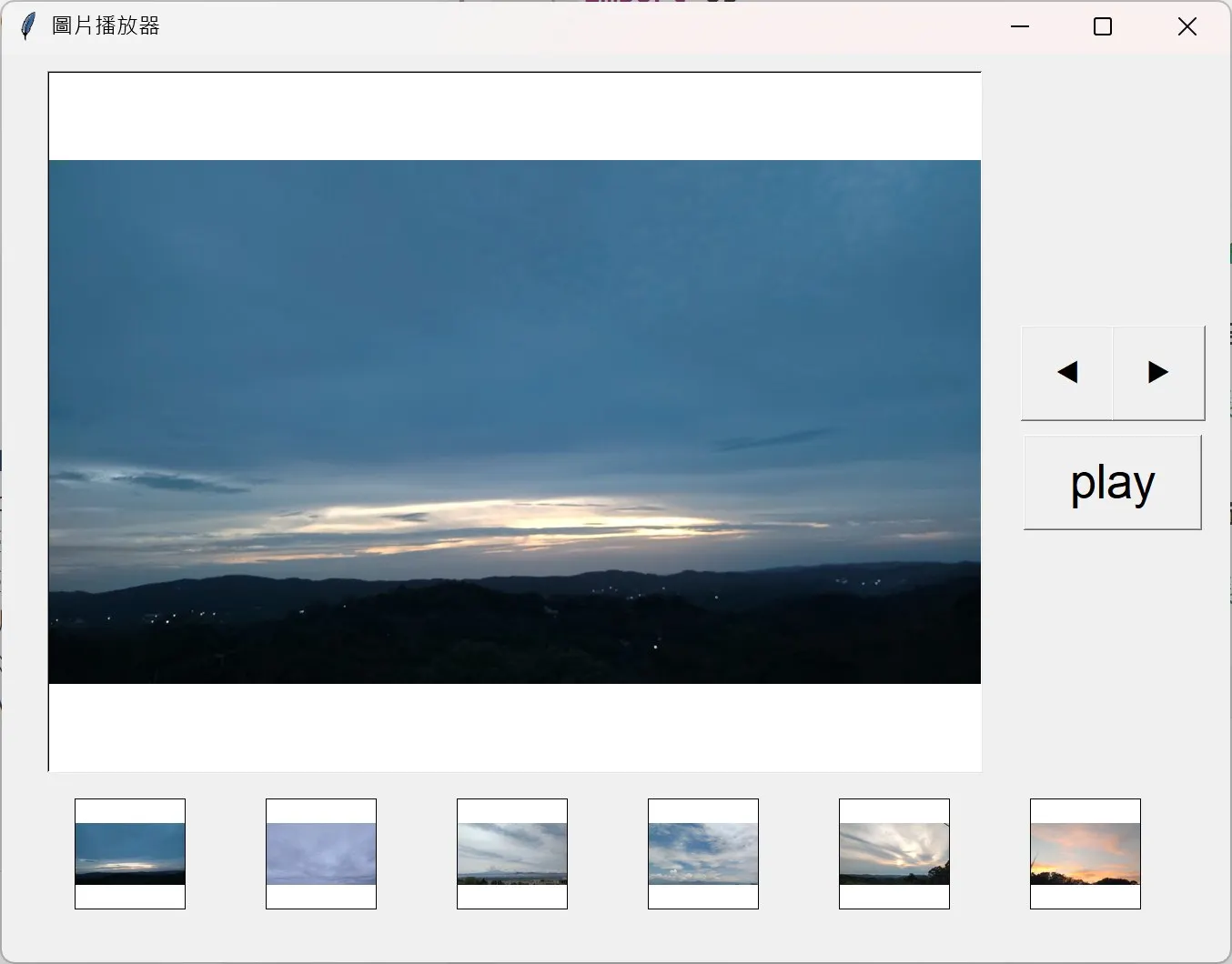
圖 3:能遵照手繪設計稿生成的圖檔播放器
圖 3 對應的原始程式碼如下所示:
PhotoPlayer1.py
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, messagebox
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
import os
import glob
class ImagePlayer:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("圖片播放器")
self.root.geometry("1400x900") # 大視窗
self.root.configure(bg="#f0f0f0")
# 選擇資料夾
self.image_folder = filedialog.askdirectory(title="請選擇圖片資料夾")
if not self.image_folder:
messagebox.showerror("錯誤", "你沒有選擇資料夾,程式將關閉")
root.destroy()
return
self.image_files = self.load_images()
if not self.image_files:
messagebox.showerror("錯誤", "資料夾中沒有支援的圖片")
root.destroy()
return
self.index = 0
self.playing = False
# 主圖顯示(最大 1024x768)
self.display_label = tk.Label(root, width=1024, height=768, bg="white", bd=2, relief="sunken")
self.display_label.place(x=50, y=20)
# 控制按鈕
self.left_button = tk.Button(root, text="◀", font=("Arial", 20), width=3, command=self.prev_image)
self.left_button.place(x=1120, y=300)
self.right_button = tk.Button(root, text="▶", font=("Arial", 20), width=3, command=self.next_image)
self.right_button.place(x=1220, y=300)
self.play_button = tk.Button(root, text="play", font=("Arial", 16), width=6, command=self.toggle_play)
self.play_button.place(x=1170, y=380)
# ✅ 縮圖區(6 張)
self.thumb_labels = []
for i in range(6): # 改為 6 張
label = tk.Label(root, width=120, height=120, bg="white", bd=1, relief="solid")
label.place(x=80 + i * 210, y=820) # 排列間距調整
label.bind("", lambda e, i=i: self.select_image_by_thumb(i))
self.thumb_labels.append(label)
self.update_thumbnails()
self.show_image()
def load_images(self):
supported_ext = ('*.jpg', '*.png', '*.gif', '*.bmp')
files = []
for ext in supported_ext:
files.extend(glob.glob(os.path.join(self.image_folder, ext)))
return sorted(files)
def show_image(self):
if not self.image_files:
return
image_path = self.image_files[self.index]
img = Image.open(image_path)
img.thumbnail((1024, 768)) # 放大主圖限制
img_tk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img)
self.display_label.config(image=img_tk)
self.display_label.image = img_tk
def update_thumbnails(self):
for i in range(6): # 6 張縮圖
label = self.thumb_labels[i]
if i < len(self.image_files):
img = Image.open(self.image_files[i])
img.thumbnail((120, 120))
img_tk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(img)
label.config(image=img_tk)
label.image = img_tk
else:
label.config(image='', text='')
def select_image_by_thumb(self, i):
if i < len(self.image_files):
self.index = i
self.show_image()
def prev_image(self):
self.index = (self.index - 1) % len(self.image_files)
self.show_image()
def next_image(self):
self.index = (self.index + 1) % len(self.image_files)
self.show_image()
def toggle_play(self):
self.playing = not self.playing
self.play_button.config(text="stop" if self.playing else "play")
if self.playing:
self.auto_play()
def auto_play(self):
if self.playing:
self.next_image()
self.root.after(1000, self.auto_play)
# ========= 主程式入口 =========
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = ImagePlayer(root)
root.mainloop()
二、影片檔播放器
我們使用以下咒語指揮 ChatGPT 生出程式碼:
(任務)產生影片播放器,要支援各種常見的影片格式
(輸出)生成 Python 程式碼
ChatGPT 生成的參考程式碼如下:
VideoPlayer.py
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
import cv2
import threading
import time
class VideoPlayer:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("影片播放器")
self.root.geometry("800x600")
self.label = tk.Label(root)
self.label.pack()
self.btn_open = tk.Button(root, text="開啟影片", command=self.load_video)
self.btn_open.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)
self.btn_play = tk.Button(root, text="播放", command=self.play_video)
self.btn_play.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)
self.btn_pause = tk.Button(root, text="暫停", command=self.pause_video)
self.btn_pause.pack(side=tk.LEFT, padx=10)
self.cap = None
self.playing = False
self.video_thread = None
def load_video(self):
filepath = filedialog.askopenfilename(
title="選擇影片",
filetypes=[("Video files", "*.mp4 *.avi *.mov *.mkv"), ("All files", "*.*")]
)
if filepath:
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(filepath)
self.playing = False
self.show_frame() # 顯示第一幀畫面
def show_frame(self):
if self.cap and self.cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = self.cap.read()
if ret:
# 轉換顏色 BGR → RGB
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = Image.fromarray(frame)
img = img.resize((800, 450)) # 調整顯示大小
imgtk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=img)
self.label.imgtk = imgtk
self.label.config(image=imgtk)
def play_video(self):
if not self.cap or not self.cap.isOpened():
return
self.playing = True
if not self.video_thread or not self.video_thread.is_alive():
self.video_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.update_frame)
self.video_thread.start()
def update_frame(self):
while self.playing and self.cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = self.cap.read()
if not ret:
break
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = Image.fromarray(frame)
img = img.resize((800, 450))
imgtk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(image=img)
self.label.imgtk = imgtk
self.label.config(image=imgtk)
time.sleep(1/30) # 假設影片為 30 FPS
def pause_video(self):
self.playing = False
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = VideoPlayer(root)
root.mainloop()
以上程式碼在 fChart 的執行結果如圖 4 所示(測試素材可由此下載):
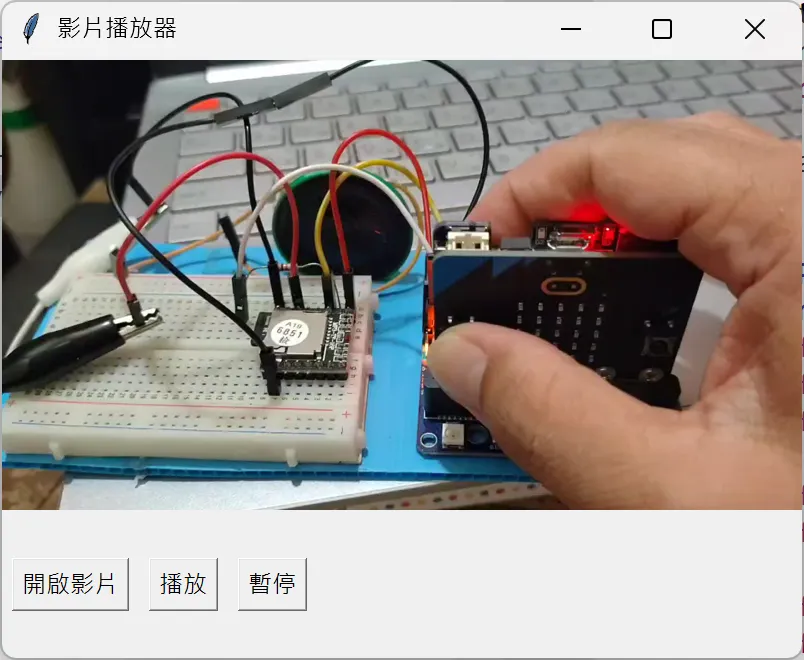
圖 4:VideoPlayer.py 的執行畫面
註:fChart 已安裝了 Python 版的 OpenCV(4.5.3.56)和 Pillow(PIL)(8.3.1)套件了(圖 5)。
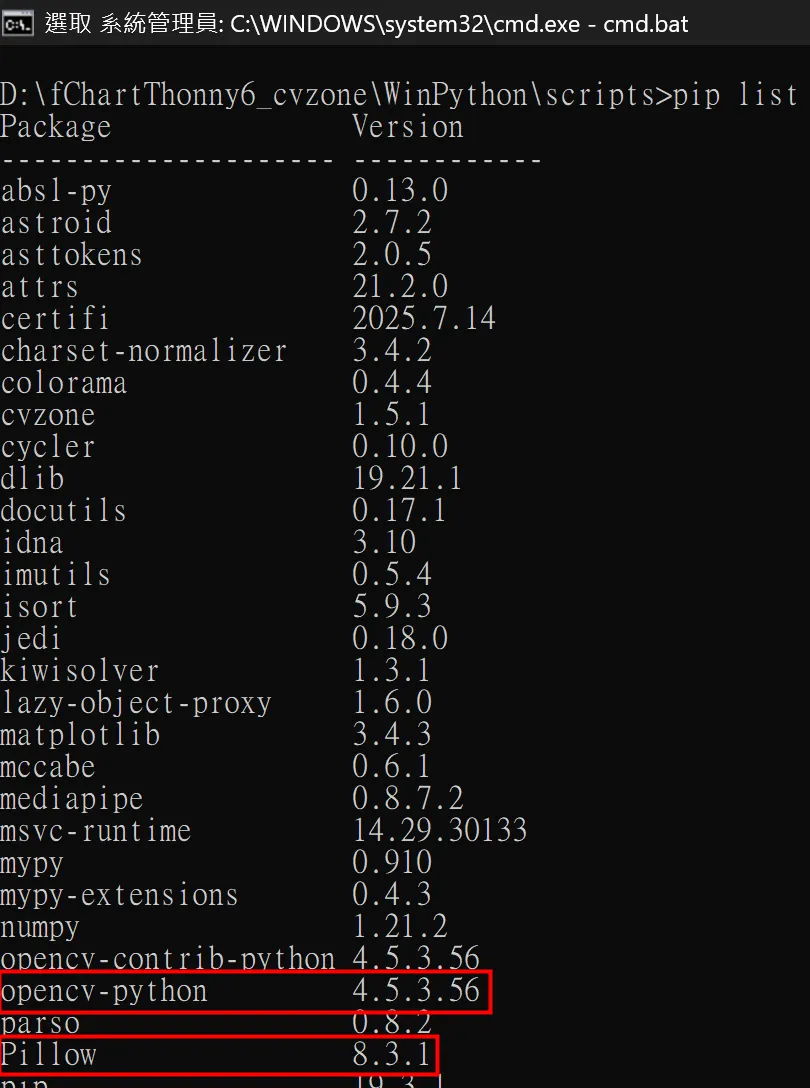
圖 5:fChart 已裝妥 Python 版的 Open CV 和 Pillow
此時,細心的讀者可能會發現:VideoPlayer.py 播放的測試影片是「有影(像)無聲(音)。
我們再詢問 ChatGPT 細究原因,它說「OpenCV 本身不支援音訊播放」並建議以下三個解決方法:
- VLC(VideoLAN Client) → 最穩定
- ffmpeg → 最常見
- moviepy → 有封裝好的音訊介面
根據 ChatGPT 的指示,先下載和安裝 VLC,我們甞試使用 VLC。接著再安裝 Python VLC 套件(pip install python-vlc)(圖 6)。
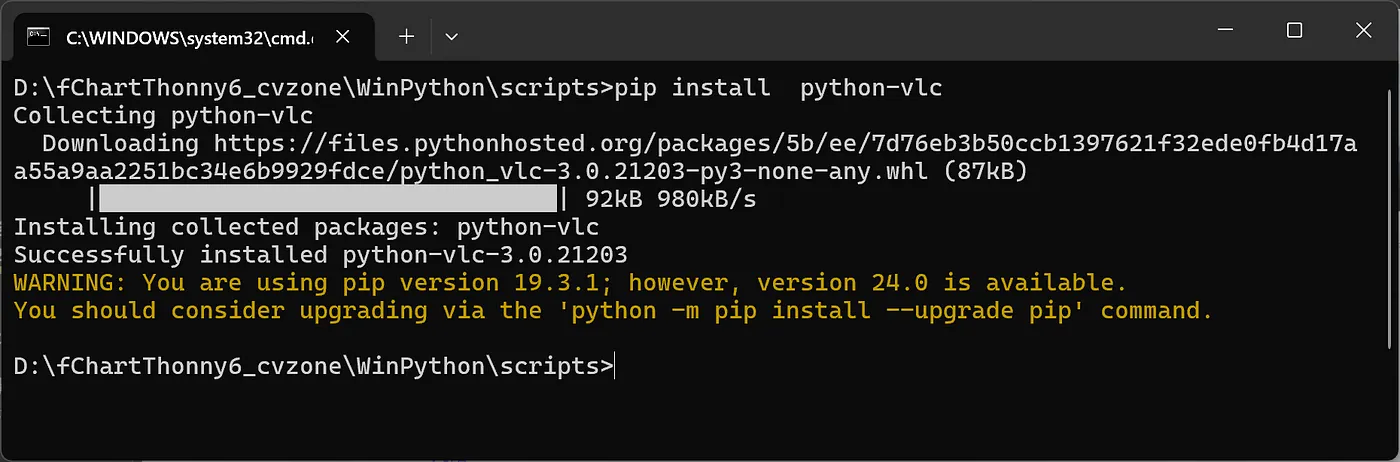
圖 6:fChart 內手動安裝 Python 版的 VLC 套件
如此就大功告成了(圖 7)!
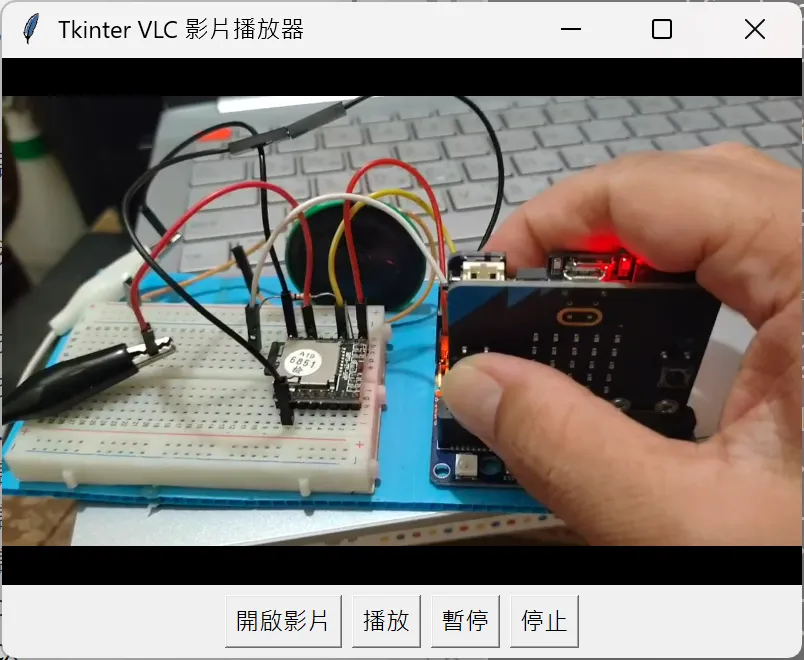
圖 7:安裝了 VLC 的影片檔播放器
參考的程式碼如下:
VideoPlayer_VLC.py
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
import vlc
import os
import platform
class VLCPlayer:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Tkinter VLC 影片播放器")
self.root.geometry("800x600")
# 建立 VLC 播放器實例
self.instance = vlc.Instance()
self.player = self.instance.media_player_new()
# 影片播放區域 Frame
self.video_panel = tk.Frame(self.root)
self.video_panel.pack(fill="both", expand=1)
# 控制按鈕區
self.btn_frame = tk.Frame(self.root)
self.btn_frame.pack(pady=10)
self.open_btn = tk.Button(self.btn_frame, text="開啟影片", command=self.open_file)
self.open_btn.grid(row=0, column=0, padx=5)
self.play_btn = tk.Button(self.btn_frame, text="播放", command=self.play)
self.play_btn.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=5)
self.pause_btn = tk.Button(self.btn_frame, text="暫停", command=self.pause)
self.pause_btn.grid(row=0, column=2, padx=5)
self.stop_btn = tk.Button(self.btn_frame, text="停止", command=self.stop)
self.stop_btn.grid(row=0, column=3, padx=5)
self.media = None
self.root.update() # 確保元件建立完成
# 取得影片播放視窗 handle,依系統設置
self.handle = self.video_panel.winfo_id()
sys_platform = platform.system()
if sys_platform == "Windows":
self.player.set_hwnd(self.handle)
elif sys_platform == "Linux":
self.player.set_xwindow(self.handle)
elif sys_platform == "Darwin": # macOS
self.player.set_nsobject(self.handle)
def open_file(self):
filepath = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=[("影片檔案", "*.mp4;*.avi;*.mov;*.mkv")])
if filepath:
self.media = self.instance.media_new(filepath)
self.player.set_media(self.media)
self.play()
def play(self):
if self.media:
self.player.play()
def pause(self):
self.player.pause()
def stop(self):
self.player.stop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 設定 VLC 的 DLL 路徑(Windows 必要)
os.environ['PATH'] = r'C:\Program Files\VideoLAN\VLC' + ';' + os.environ['PATH']
root = tk.Tk()
app = VLCPlayer(root)
root.mainloop()
三、音檔播放器
在 ChatGPT 中下達以下咒語:
(任務)Tkinter 視窗版的 MP3 播放器,選擇多首 MP3 曲目後,顯示在畫面上,連續隨機播放這些曲目不停止。正在播放的曲目要用顏色標記
(輸出)Python 程式碼
有了以上第二節的經驗,依照 ChatGPT 的指示,先裝妥 pygame 套件(pip install pygame)後就能生成這個播器的參考程式碼(No-threading.py)。
詳細的操做步驟及更進一步的程式碼拆解請詳参我們先前的拙著《台語 MP3 播放器(Claude + Python):弓(kin)蕉的台語秘密》。
[1]六種授權條款。
(作者為本刊專欄作家,本文同步表於作者部落格,原文連結;責任編輯:謝涵如)
- 用GenAI自動拆解程式碼學習:GenAI時代的新程式學習法 - 2025/12/29
- 「動手」之前 你需要了解電腦系統的基礎知識點! - 2025/11/28
- GenAI拆解學習:以「健康手環監測系統」示例 - 2025/10/23
訂閱MakerPRO知識充電報
與40000位開發者一同掌握科技創新的技術資訊!



