作者:高煥堂
接續本文上集,我們複習一下GAN的兩個角色:生成器(G)和判別器(D)。
準備訓練數據:使用ShapeNet數據集
GAN(生成對抗網)是由蒙特利爾大學的Ian Goodfellow在2014年提出來的神經網路模型。GAN通常包含兩個角色,兩者互相較量(對抗),但又展現出教學相長,共同成長的美好機制和效果。這兩個角色就是:判別者(Discriminator)與生成者(Generator)。
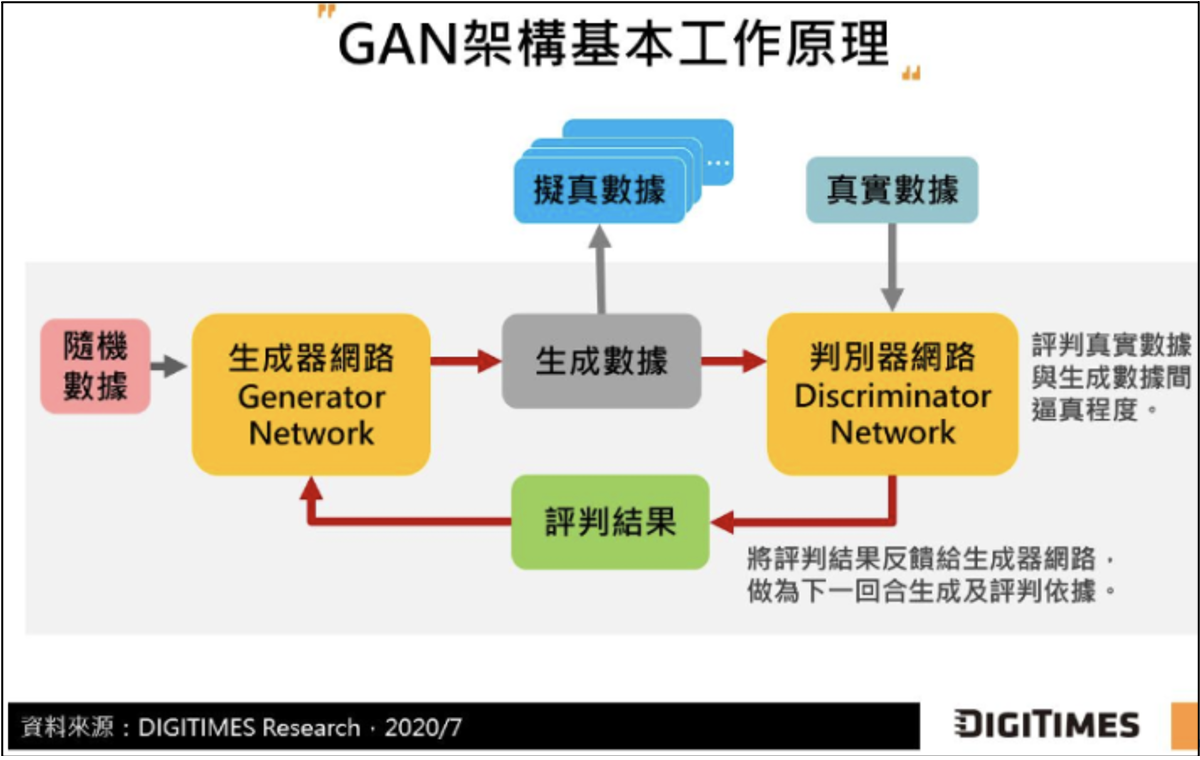
其中的判別者(D)是老師角色,而生成者(G)則是學生角色。老師引導學生創作,兩者互相較量(對抗),但又展現出教學相長的效果。例如,在圖像渲染的應用上,它們的功能分別是:
- G(學生)負責生成圖片。它接收一個隨機噪音(z),或者其他條件(如黑白底圖或邊框),然後基于這個噪音或條件來生成新圖片。
- D(老師)負責辨別一張圖片的真或假。它的輸入是一張圖片,進行辨別之後,輸出其判斷爲真品或假品的概率。如果輸出值愈接近于1,代表其爲真品的概率愈大;而當輸出值愈接0,代表其爲假品的概率愈大。
在GAN模型的訓練過程中,我們會拿真品來輸入給D,也會拿由G生成的假品來輸入給D。其目的是要訓練D,以便提升它判斷圖片真或假的能力。
如果D判斷正確,表示G(學生)生成的新作品(假品),被D識破了,這意味著G的作品不够逼真,此時G就會依據D的反饋而調整其參數,因而G就成長了。反之,如果D判斷錯誤,表示D的辨別能力不足,例如被G騙了(將假品誤判爲真品),于是D就會調整其參數,因而D也成長了。
這樣的訓練過程,持續重複下去,GAN裏的兩個角色,互相較量(對抗),展現出了教學相長的美好效果。最後,G大幅成長了,繪製出來非常逼真的作品(假品)了。
程式4:定義GAN的生成器,並進行訓練
定義並單獨訓練生成器(G);暫時不訓練判別器(D)。
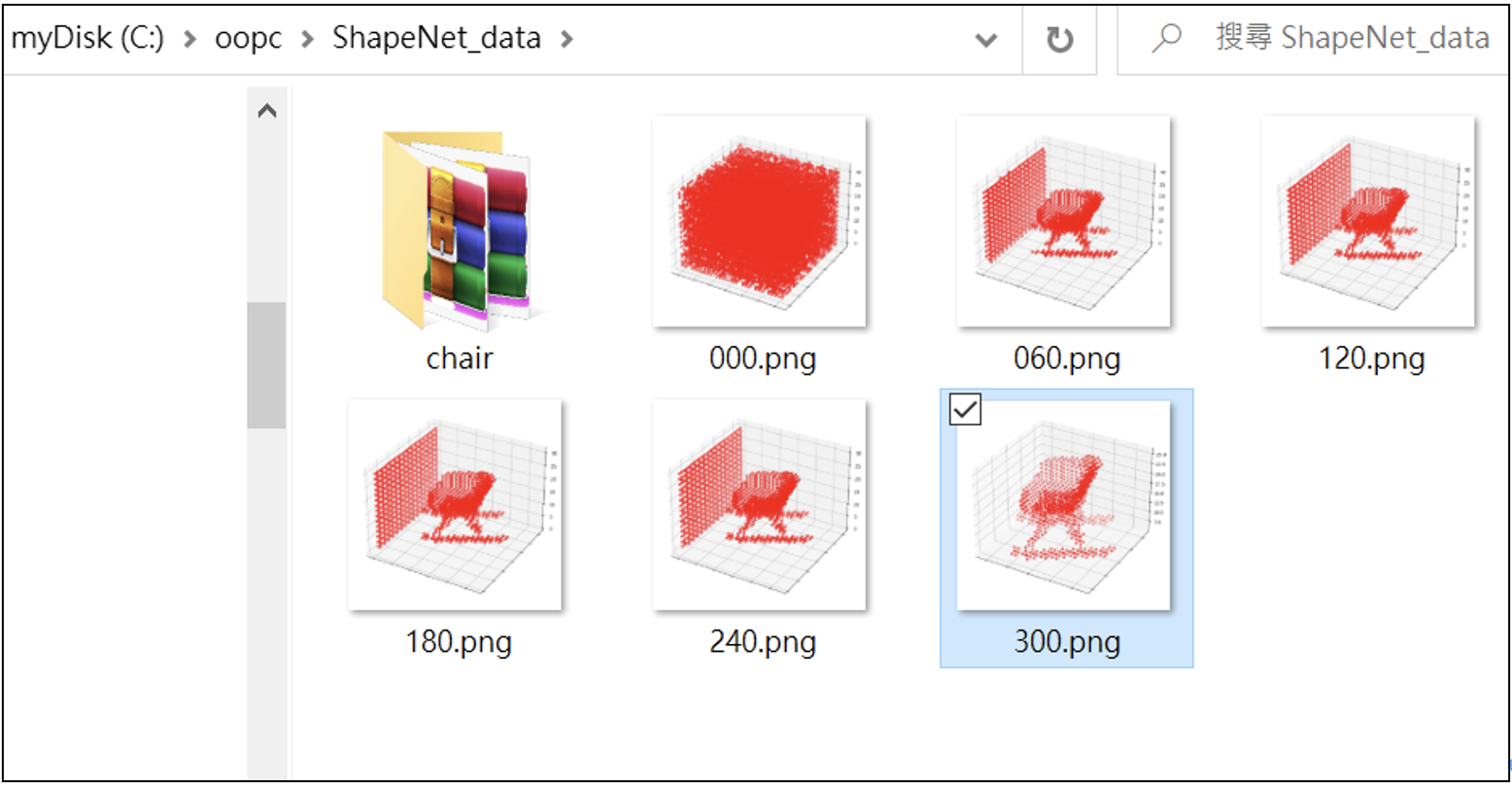
由生成器(Generator)自己學習重建點雲3D圖像,訓練300回合。並且,把訓練過程的圖像(儲存)顯示出來。在訓練過程中,每60回合儲存一次。程式碼如下:
# paa_GAN_005.py
import numpy as np
import os
import torch
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.optimizer as optim
from paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoader
import scipy.ndimage as nd
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data_dir = 'c:/oopc/ShapeNet_data/chair/train/'
file_list = [os.path.join(data_dir, name)
for name in os.listdir(data_dir)
if name.endswith('.mat')]
print(len(file_list))
#-----------------------------------------------------
nchw = [1,32,32,32]
# 讀取一個3D的*.mat檔案
def getVoxelFromMat(file_path):
voxels = sio.loadmat(file_path)['instance']
voxels = np.pad(voxels, (1, 1), 'constant', constant_values=(0, 0))
if nchw[-1] != 32:
ratio = nchw[-1] / 32.
voxels = nd.zoom(voxels, (ratio, ratio, ratio),
mode='constant', order=0)
return voxels
def SavePloat_Voxels(voxels, path, iteration):
voxels = voxels.__ge__(0.5)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(32, 16))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 4)
gs.update(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.05)
for i, sample in enumerate(voxels):
x, y, z = sample.nonzero()
ax = plt.subplot(gs[i], projection='3d')
ax.scatter(x, y, z, zdir='z', c='red')
ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.set_yticklabels([])
plt.savefig(path + '/{}.png'.format(str(iteration).zfill(3)), bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
#---------------------------------
class ShapeNetDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self):
self.filenames = file_list
def __getitem__(self, index):
fna = self.filenames[index]
volume = np.asarray(getVoxelFromMat(fna), dtype=np.float32)
return paddle.to_tensor(volume)
def __len__(self):
return len( self.filenames)
#---------------------------------------
batch_size = 1
d_thresh = 0.8
z_dim = 100
f_dim = 32
g_lr = 0.0025
d_lr = 0.0005
beta = (0.5, 0.999)
cube_len = 32
leak_value = 0.2
bias = False
def get_noise():
z = paddle.normal(shape=[batch_size, z_dim])
z = paddle.to_tensor(z)
return z
class Generator(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.cube_len = cube_len
padd = (0, 0, 0)
if self.cube_len == 32:
padd = (1,1,1)
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(z_dim, f_dim * 8,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*8),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 8, f_dim * 4,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*4),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 4, f_dim * 2,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*2),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 2, f_dim,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim),
)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim, 1,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = paddle.reshape(x, shape=[-1, z_dim, 1, 1, 1])
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
return x
#----------------------------------------------------
G = Generator()
optimizer_g = optim.Adam(learning_rate=g_lr, parameters=G.parameters())
L1_loss = nn.L1Loss()
#-------------------------------------------------
dataset = ShapeNetDataset()
real_vx = dataset[0]
real_vx = real_vx.unsqueeze(0)
print('開始訓練 300回合...')
num_epochs = 300
for ep in range(num_epochs+1):
#print(ep)
G.train()
noise = get_noise()
gen_vx = G(noise)
loss_g = L1_loss(gen_vx, real_vx) * 100
loss_g.backward()
optimizer_g.step()
optimizer_g.clear_grad()
if(ep%60 == 0):
gen_vx = gen_vx.squeeze(0)
vx = gen_vx.numpy()
SavePloat_Voxels(vx, 'c:/oopc/ShapeNet_data/', ep)
#-------------------------------------
#END
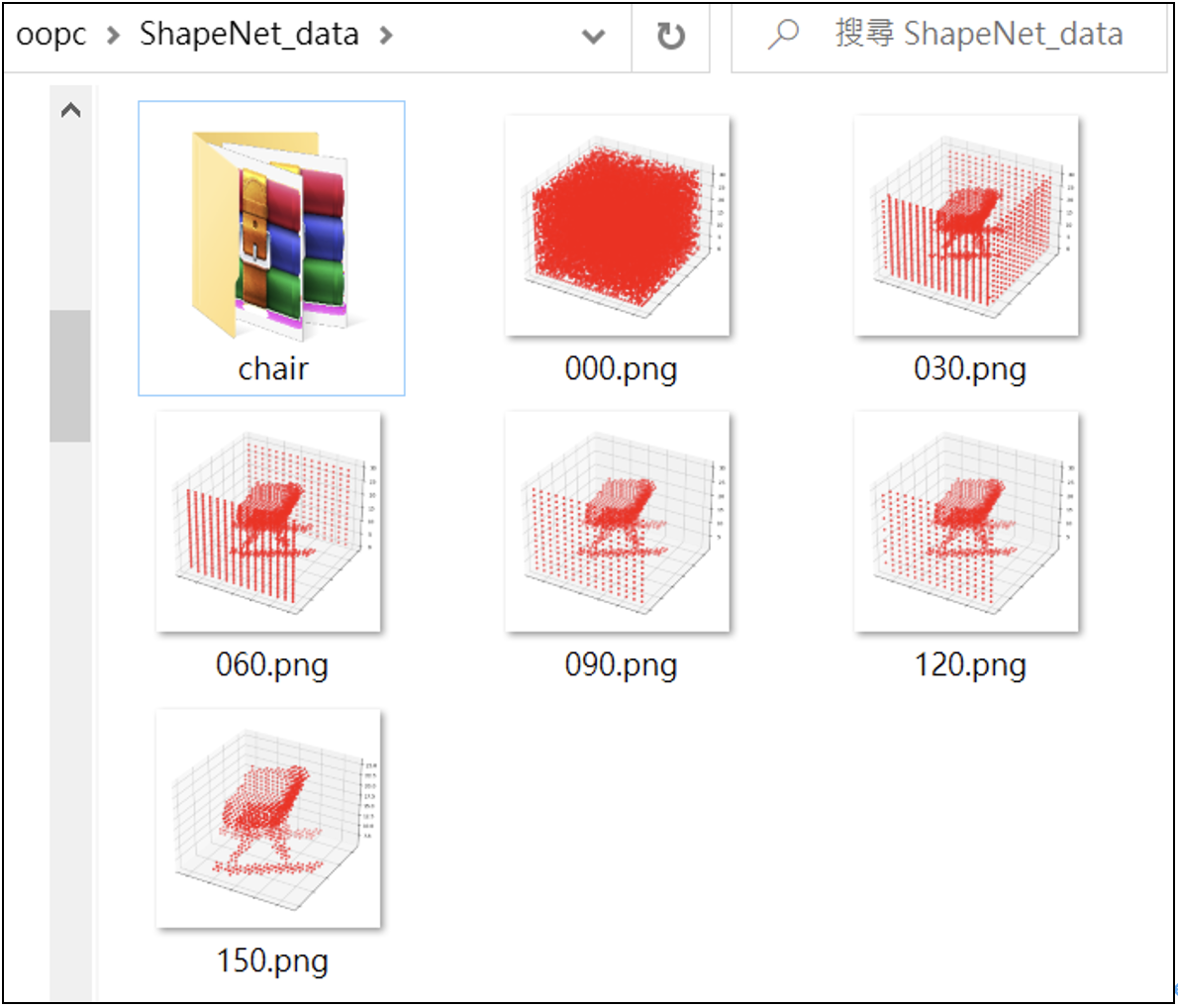
在訓練生成器(G)共300回合的在訓練過程中,每60回合儲存一次寫入圖檔(儲存於/ShapeNet_data/裡),如下:
程式5:設計判別器,並且進行訓練
添加另一個角色:判別器D(Discriminator)。D和G一起訓練,相互成長。
這是典型的GAN訓練模式。此程式也會把典型GAN訓練過程的圖像儲存起來。以便給您觀察GAN訓練過程的圖像生成過程。程式碼如下:
這是典型的GAN訓練流程,訓練150回合。在訓練過程中,所生成的一系列圖像為:# paa_GAN_009.py
import numpy as np
import os
import torch
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.optimizer as optim
from paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoader
import scipy.ndimage as nd
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data_dir = 'c:/oopc/ShapeNet_data/chair/train/'
file_list = [os.path.join(data_dir, name)
for name in os.listdir(data_dir)
if name.endswith('.mat')]
print(len(file_list))
#-----------------------------------------------------
nchw = [1,32,32,32]
# 讀取一個3D的*.mat檔案
def getVoxelFromMat(file_path):
voxels = sio.loadmat(file_path)['instance']
voxels = np.pad(voxels, (1, 1), 'constant', constant_values=(0, 0))
if nchw[-1] != 32:
ratio = nchw[-1] / 32.
voxels = nd.zoom(voxels, (ratio, ratio, ratio),
mode='constant', order=0)
return voxels
def SavePloat_Voxels(voxels, path, iteration):
voxels = voxels.__ge__(0.5)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(32, 16))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 4)
gs.update(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.05)
for i, sample in enumerate(voxels):
x, y, z = sample.nonzero()
ax = plt.subplot(gs[i], projection='3d')
ax.scatter(x, y, z, zdir='z', c='red')
ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.set_yticklabels([])
plt.savefig(path + '/{}.png'.format(str(iteration).zfill(3)), bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
#---------------------------------
class ShapeNetDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self):
self.filenames = file_list
def __getitem__(self, index):
fna = self.filenames[index]
volume = np.asarray(getVoxelFromMat(fna), dtype=np.float32)
return paddle.to_tensor(volume)
def __len__(self):
return len( self.filenames)
#---------------------------------------
batch_size = 1
d_thresh = 0.8
z_dim = 100
f_dim = 32
g_lr = 0.0025
d_lr = 0.0004
beta = (0.5, 0.999)
cube_len = 32
leak_value = 0.2
bias = False
#-------------------------------------
class Discriminator(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(1, f_dim,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim, f_dim*2,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*2),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim*2, f_dim*4,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*4),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim*4, f_dim*8,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*8),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim*8, 1,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = paddle.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 1, cube_len, cube_len, cube_len])
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
x = x.squeeze(0).squeeze(0).squeeze(0)
return x
#----------------------------------------------------
def get_noise():
z = paddle.normal(shape=[batch_size, z_dim])
return z
class Generator(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.cube_len = cube_len
padd = (0, 0, 0)
if self.cube_len == 32:
padd = (1,1,1)
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(z_dim, f_dim * 8,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*8),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 8, f_dim * 4,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*4),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 4, f_dim * 2,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*2),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 2, f_dim,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim),
)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim, 1,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = paddle.reshape(x, shape=[-1, z_dim, 1, 1, 1])
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
return x
#----------------------------------------------------
D = Discriminator()
G = Generator()
optimizer_d = optim.Adam(learning_rate=d_lr, parameters=D.parameters())
optimizer_g = optim.Adam(learning_rate=g_lr, parameters=G.parameters())
BCE_loss = nn.BCELoss()
L1_loss = nn.L1Loss()
#-------------------------------------------------
dataset = ShapeNetDataset()
real_vx = dataset[0]
X = real_vx.unsqueeze(0)
num_epochs = 150
for ep in range(num_epochs+1):
D.train()
d_real = D(X)
true_label = paddle.ones_like(d_real)
d_real_loss = BCE_loss(d_real, true_label)
noise = get_noise()
fake = G(noise)
fake = fake.squeeze(0)
d_fake = D(fake)
new_label = paddle.zeros_like(d_fake)
d_fake_loss = BCE_loss(d_fake, new_label)
d_loss = (d_real_loss + d_fake_loss) * 0.5
d_loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
optimizer_d.step()
#---- Train G --------------------------------
G.train()
d_fake = D(fake)
true_label = paddle.ones_like(d_fake)
g_loss = BCE_loss(d_fake, true_label)
#loss_L1 = L1_loss(fake, X) * 100
#g_loss = g_loss + loss_L1
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_g.step()
optimizer_d.clear_grad()
optimizer_g.clear_grad()
if(ep%30 == 0):
# =============== each epoch save model or save image
print('epoch:', ep, ' images_saved...')
samples = fake.numpy()
SavePloat_Voxels(samples, 'c:/oopc/ShapeNet_data/', ep)
#---------------------------------
#END
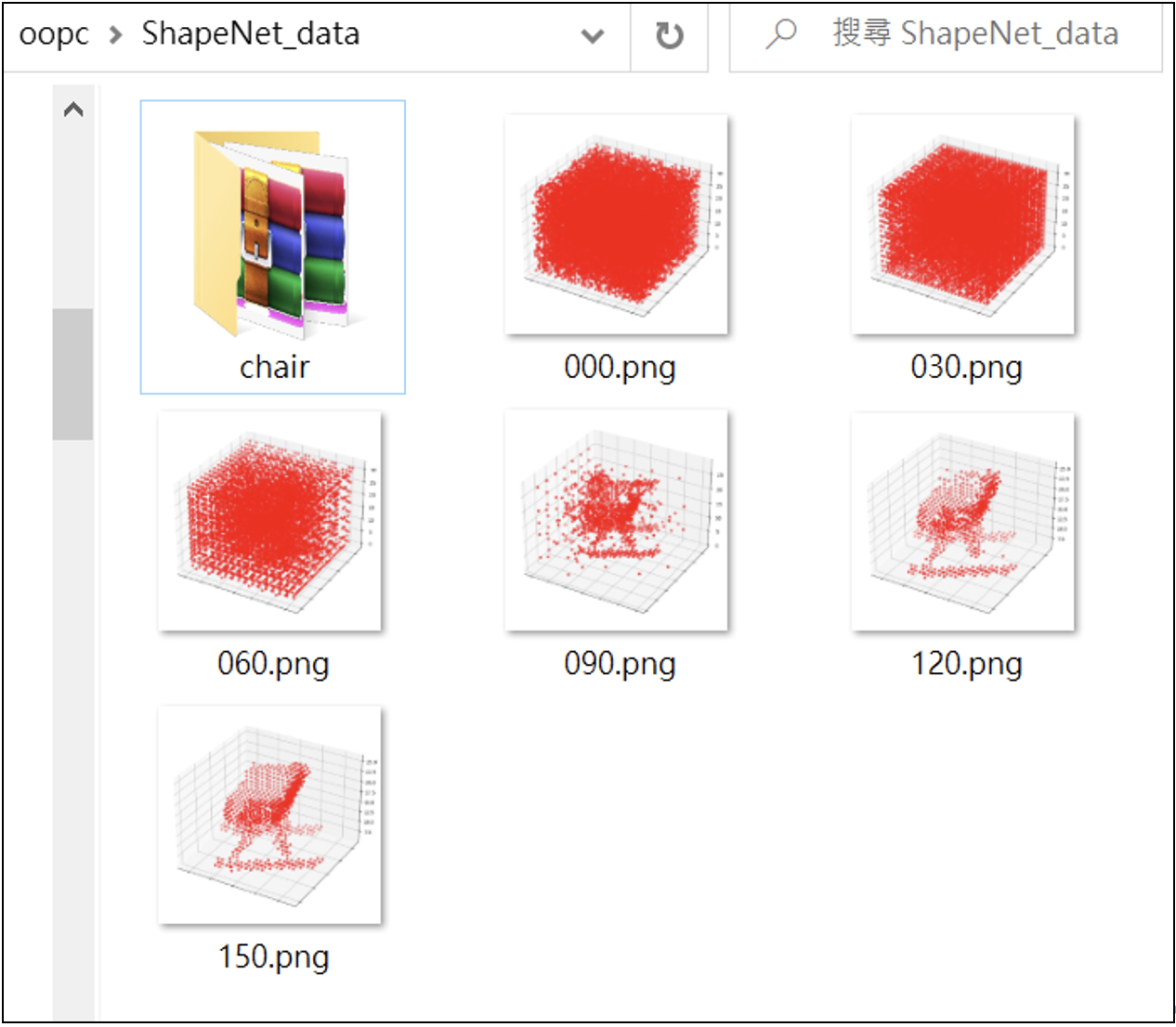
放大圖像:
程式6:優化GAN模型的學習能力
添加了兩行程式碼:
#=====================================
loss_L1 = L1_loss(fake, X) * 100
g_loss = g_loss + loss_L1
#=====================================
程式碼如下:
# paa_GAN_010.py
import numpy as np
import os
import torch
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import paddle.optimizer as optim
from paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoader
import scipy.ndimage as nd
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data_dir = 'c:/oopc/ShapeNet_data/chair/train/'
file_list = [os.path.join(data_dir, name)
for name in os.listdir(data_dir)
if name.endswith('.mat')]
print(len(file_list))
#-----------------------------------------------------
nchw = [1,32,32,32]
# 讀取一個3D的*.mat檔案
def getVoxelFromMat(file_path):
voxels = sio.loadmat(file_path)['instance']
voxels = np.pad(voxels, (1, 1), 'constant', constant_values=(0, 0))
if nchw[-1] != 32:
ratio = nchw[-1] / 32.
voxels = nd.zoom(voxels, (ratio, ratio, ratio),
mode='constant', order=0)
return voxels
def SavePloat_Voxels(voxels, path, iteration):
voxels = voxels.__ge__(0.5)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(32, 16))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 4)
gs.update(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.05)
for i, sample in enumerate(voxels):
x, y, z = sample.nonzero()
ax = plt.subplot(gs[i], projection='3d')
ax.scatter(x, y, z, zdir='z', c='red')
ax.set_xticklabels([])
ax.set_yticklabels([])
plt.savefig(path + '/{}.png'.format(str(iteration).zfill(3)), bbox_inches='tight')
plt.close()
#---------------------------------
class ShapeNetDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self):
self.filenames = file_list
def __getitem__(self, index):
fna = self.filenames[index]
volume = np.asarray(getVoxelFromMat(fna), dtype=np.float32)
return paddle.to_tensor(volume)
def __len__(self):
return len( self.filenames)
#---------------------------------------
batch_size = 1
d_thresh = 0.8
z_dim = 100
f_dim = 32
g_lr = 0.0025
d_lr = 0.0004
beta = (0.5, 0.999)
cube_len = 32
leak_value = 0.2
bias = False
#-------------------------------------
class Discriminator(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(1, f_dim,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim, f_dim*2,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*2),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim*2, f_dim*4,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*4),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim*4, f_dim*8,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*8),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3D(f_dim*8, 1,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
bias_attr=bias, padding=1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = paddle.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 1, cube_len, cube_len, cube_len])
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
x = x.squeeze(0).squeeze(0).squeeze(0)
return x
#----------------------------------------------------
def get_noise():
z = paddle.normal(shape=[batch_size, z_dim])
return z
class Generator(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.cube_len = cube_len
padd = (0, 0, 0)
if self.cube_len == 32:
padd = (1,1,1)
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(z_dim, f_dim * 8,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*8),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 8, f_dim * 4,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*4),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 4, f_dim * 2,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim*2),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim * 2, f_dim,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.BatchNorm3D(f_dim),
)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3DTranspose(f_dim, 1,
kernel_size=4, stride=2,
padding=(1,1,1), bias_attr=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
x = paddle.reshape(x, shape=[-1, z_dim, 1, 1, 1])
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
return x
#----------------------------------------------------
D = Discriminator()
G = Generator()
optimizer_d = optim.Adam(learning_rate=d_lr, parameters=D.parameters())
optimizer_g = optim.Adam(learning_rate=g_lr, parameters=G.parameters())
BCE_loss = nn.BCELoss()
L1_loss = nn.L1Loss()
#-------------------------------------------------
dataset = ShapeNetDataset()
real_vx = dataset[0]
X = real_vx.unsqueeze(0)
num_epochs = 150
for ep in range(num_epochs+1):
D.train()
d_real = D(X)
true_label = paddle.ones_like(d_real)
d_real_loss = BCE_loss(d_real, true_label)
noise = get_noise()
fake = G(noise)
fake = fake.squeeze(0)
d_fake = D(fake)
new_label = paddle.zeros_like(d_fake)
d_fake_loss = BCE_loss(d_fake, new_label)
d_loss = (d_real_loss + d_fake_loss) * 0.5
d_loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
optimizer_d.step()
#---- Train G --------------------------------
G.train()
d_fake = D(fake)
true_label = paddle.ones_like(d_fake)
g_loss = BCE_loss(d_fake, true_label)
#=====================================
loss_L1 = L1_loss(fake, X) * 100
g_loss = g_loss + loss_L1
#=====================================
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_g.step()
optimizer_d.clear_grad()
optimizer_g.clear_grad()
if(ep%30 == 0):
# =============== each epoch save model or save image
print('epoch:', ep, ' images_saved...')
samples = fake.numpy()
SavePloat_Voxels(samples, 'c:/oopc/ShapeNet_data/', ep)
#----------------------
#END
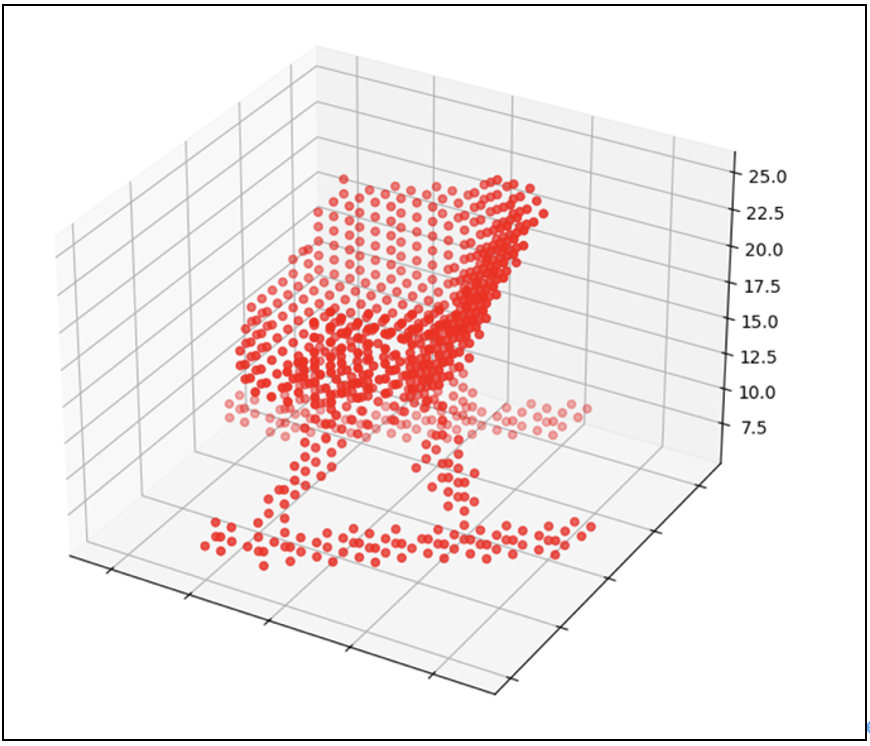
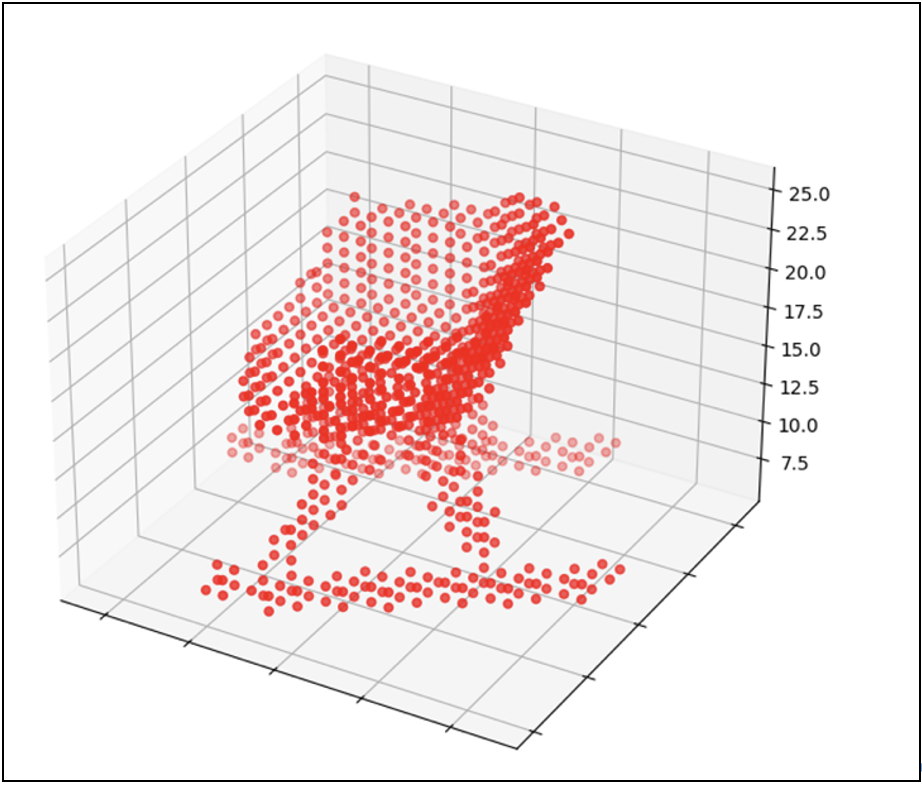
生成圖像為:
放大圖像:
大功告成。
(責任編輯:謝涵如)
- LoRA微調三步驟:以大語言模型MT5為例 - 2024/05/02
- 為什麼Gemma採取Decoder-Only Transformer架構呢? - 2024/04/08
- 如何從0訓練企業自用Gemma模型 - 2024/04/03
訂閱MakerPRO知識充電報
與40000位開發者一同掌握科技創新的技術資訊!



