作者:曹永忠
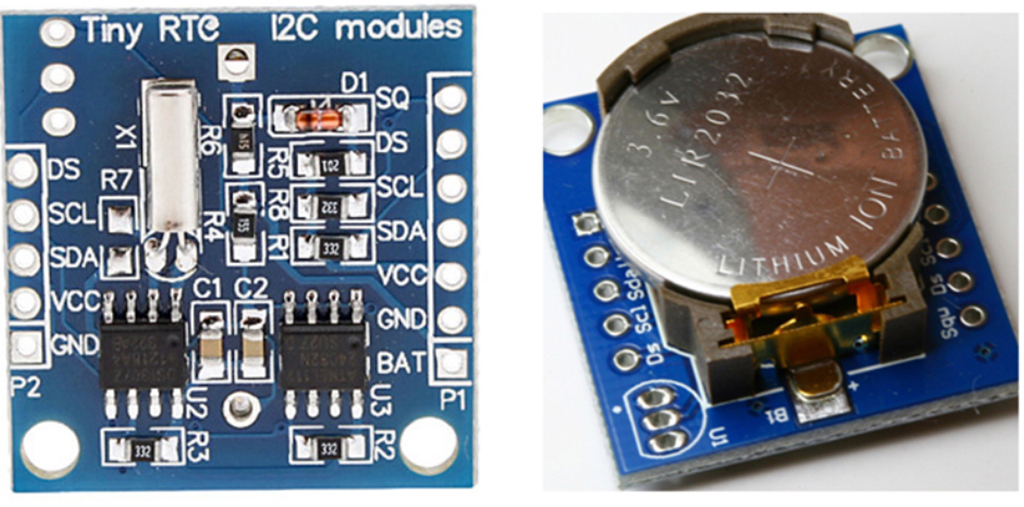
前文介紹 RTC 時鐘模組具備時間功能,並且為了斷電時仍然可以保留時間,補足Ameba開發板並沒有內置時鐘(Internal Clock)的問題,可以見到 「Tiny RTC I2C 時鐘模組」的外觀圖,模組採用DS1307晶片,若讀者需要更詳盡的資料,請參考「Arduino投幣計時器(網路篇)」,內容關於RTC 時鐘模組。
RTC時鐘模組的介紹與描述
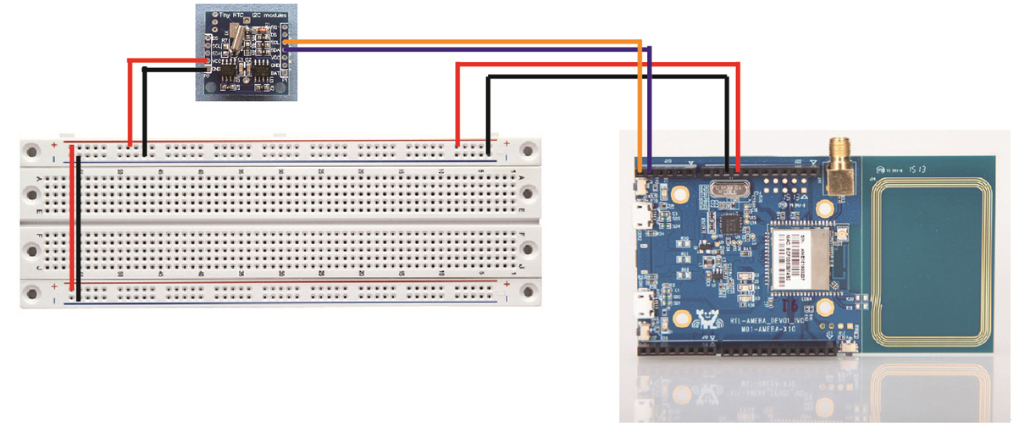
如下圖所示,我們可以參考時鐘模組之電路連接圖,先將電路連接完善後,撰寫與測試下列「Tiny RTC I2C 時鐘模組」測試程式。
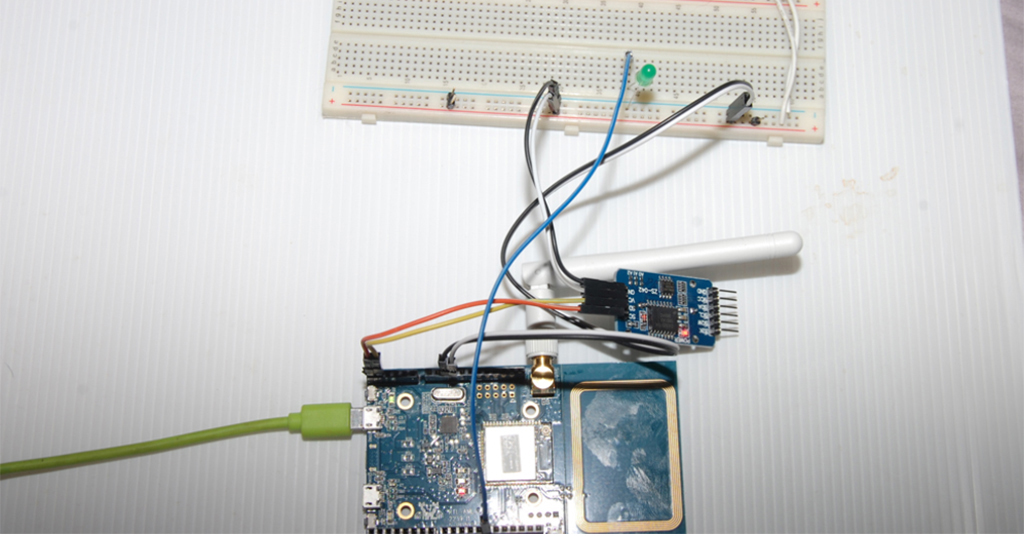
在完成上圖所示之時鐘模組之電路連接之後,如下圖所示,完成時鐘模組電路實際組裝的工作。
RTC模組的校時問題
我們發現,若裝設新的開發板或不同時間點設置新裝置,必須透過使用者重新設定時間,或是修改程式;因為「RTC 時鐘模組」的初始化時間是寫在Ameba開發板的程式內,必須重新編譯程式並上傳,這樣是非常不方便的。
若我們具有自動校時的功能,完全不需使用者手動設定或重新更新系統軟體,就可以達到正確時間校時的機制,這樣才能更簡單的產業化應用,由於目前網路校時非常的方便,所以我們可以透過網路校時的方式來實踐這個機制,或許是一個相當完善的解決方案。
Ameba的WiFi功能
Ameba開發板是一塊「IOT Wi-Fi微型化模組」(RTL8711AF and RTL8195AM),內建 ARM Cortex-M3 CPU、記憶體,同時還配置了完整的無線網路協議,包含:SSL硬體加速電路、UART、 I2C、 SPI、PWM ,以及高速的 SDIO 接口等各式序列介面(如下圖所示)。
Ameba開發板核心晶片「RTL8195AM」規格
Ameba開發板使用「RTL8195AM」為開發板核心晶片,功能強大,其下為晶片的基本規格:
- 32-bit 166MHz ARM Cortex-M3 CPU
- 內建 低功耗 802.11 b/g/n 2.4G 無線 Wi-Fi
- 內建 NFC
- 介面支援 : GPIO / PWM / SPI / I2C / ADC / DAC / UART
- Crypto HW engine : 可做硬體加解密, 支援 MD5/ SHA-1 / SHA2-256 / DES / 3DES / AES
- IC 本身有 512K RAM, 另外模組包含 2M SDRAM / 16M bit flash
Ameba開發板的規格
Ameba開發板具有強大的功能,並內含WiFi上網功能,其下為基本規格:
- 與Arduino UNO開發板相容,可支援大多數 Arduino 擴充板(Shield),如DfRobot的 LCD Keypad shield…等等
- 含一個 NXP LPC11U35 cortex-M0 IC,具備下列功能:
- 不須使用 JLINK 可直接透過 USB傳入程式image檔
- 不須使用USB序列傳輸線,UART即可使用將訊息傳給開發用的電腦
取得網路校時時間資料
將Ameba開發板的驅動程式安裝好之後,我們打開開發工具「Sketch IDE」整合開發軟體撰寫一段程式,如下表所示之網路校時測試程式,就可以透過Ameba WiFi模組取得網路校時時間。
網路校時測試程式(UdpNtpClient)
#include "PMType.h"
#include
#include
#include
uint8_t MacData[6];
char ssid[] = "TSAO"; // your network SSID (name)
char pass[] = "TSAO1234"; // your network password
char server[] = "gpssensor.ddns.net"; // the MQTT server of LASS
#define MAX_CLIENT_ID_LEN 10
#define MAX_TOPIC_LEN 50
char clientId[MAX_CLIENT_ID_LEN];
char outTopic[MAX_TOPIC_LEN];
IPAddress Meip ,Megateway ,Mesubnet ;
String MacAddress ;
int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS;
WiFiUDP Udp;
const char ntpServer[] = "pool.ntp.org";
const long timeZoneOffset = 28800L;
const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time stamp is in the first 48 bytes of the message
const byte nptSendPacket[ NTP_PACKET_SIZE] = {
0xE3, 0x00, 0x06, 0xEC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x31, 0x4E, 0x31, 0x34,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
};
byte ntpRecvBuffer[ NTP_PACKET_SIZE ];
#define LEAP_YEAR(Y) ( ((1970+Y)>0) && !((1970+Y)%4) && ( ((1970+Y)%100) || !((1970+Y)%400) ) )
static const uint8_t monthDays[]={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; // API starts months from 1, this array starts from 0
uint32_t epochSystem = 0; // timestamp of system boot up
unsigned long epoch ;
int NDPyear, NDPmonth, NDPday, NDPhour, NDPminute, NDPsecond;
void setup() {
MacAddress = GetWifiMac() ;
ShowMac() ;
initializeWiFi();
delay(1500);
}
void loop() { // run over and over
ShowNTPDateTime() ;
delay(6000); // delay 1 minute for next measurement
}
void ShowNTPDateTime()
{
retrieveNtpTime() ;
getCurrentTime(epoch+timeZoneOffset, &NDPyear, &NDPmonth, &NDPday, &NDPhour, &NDPminute, &NDPsecond);
//ttt->year = NDPyear ;
Serial.print("NDP Date is :");
Serial.print(StringDate(NDPyear,NDPmonth,NDPday));
Serial.print("and ");
Serial.print("NDP Time is :");
Serial.print(StringTime(NDPhour,NDPminute,NDPsecond));
Serial.print("\n");
}
void ShowMac()
{
Serial.print("MAC:");
Serial.print(MacAddress);
Serial.print("\n");
}
void ShowInternetStatus()
{
if (WiFi.status())
{
Meip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print("Get IP is:");
Serial.print(Meip);
Serial.print("\n");
}
else
{
Serial.print("DisConnected:");
Serial.print("\n");
}
}
String StringDate(int yyy,int mmm,int ddd) {
String ttt ;
//nowT = now;
ttt = print4digits(yyy) + "-" + print2digits(mmm) + "-" + print2digits(ddd) ;
return ttt ;
}
String StringTime(int hhh,int mmm,int sss) {
String ttt ;
ttt = print2digits(hhh) + ":" + print2digits(mmm) + ":" + print2digits(sss) ;
return ttt ;
}
String print2digits(int number) {
String ttt ;
if (number >= 0 && number < 10) { ttt = String("0") + String(number); } else { ttt = String(number); } return ttt ; } String print4digits(int number) { String ttt ; ttt = String(number); return ttt ; } String GetWifiMac() { String tt ; String t1,t2,t3,t4,t5,t6 ; WiFi.status(); //this method must be used for get MAC WiFi.macAddress(MacData); Serial.print("Mac:"); Serial.print(MacData[0],HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[1],HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[2],HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[3],HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[4],HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[5],HEX) ; Serial.print("~"); t1 = print2HEX((int)MacData[0]); t2 = print2HEX((int)MacData[1]); t3 = print2HEX((int)MacData[2]); t4 = print2HEX((int)MacData[3]); t5 = print2HEX((int)MacData[4]); t6 = print2HEX((int)MacData[5]); tt = (t1+t2+t3+t4+t5+t6) ; Serial.print(tt); Serial.print("\n"); return tt ; } String print2HEX(int number) { String ttt ; if (number >= 0 && number < 16)
{
ttt = String("0") + String(number,HEX);
}
else
{
ttt = String(number,HEX);
}
return ttt ;
}
// send an NTP request to the time server at the given address
void retrieveNtpTime() {
Serial.println("Send NTP packet");
Udp.beginPacket(ntpServer, 123); //NTP requests are to port 123
Udp.write(nptSendPacket, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
Udp.endPacket();
if(Udp.parsePacket()) {
Serial.println("NTP packet received");
Udp.read(ntpRecvBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read the packet into the buffer
unsigned long highWord = word(ntpRecvBuffer[40], ntpRecvBuffer[41]);
unsigned long lowWord = word(ntpRecvBuffer[42], ntpRecvBuffer[43]);
unsigned long secsSince1900 = highWord << 16 | lowWord; const unsigned long seventyYears = 2208988800UL; // epoch = secsSince1900 - seventyYears + timeZoneOffset ; epoch = secsSince1900 - seventyYears ; epochSystem = epoch - millis() / 1000; } } void getCurrentTime(unsigned long epoch, int *year, int *month, int *day, int *hour, int *minute, int *second) { int tempDay = 0; *hour = (epoch % 86400L) / 3600; *minute = (epoch % 3600) / 60; *second = epoch % 60; *year = 1970; *month = 0; *day = epoch / 86400; for (*year = 1970; ; (*year)++) { if (tempDay + (LEAP_YEAR(*year) ? 366 : 365) > *day) {
break;
} else {
tempDay += (LEAP_YEAR(*year) ? 366 : 365);
}
}
tempDay = *day - tempDay; // the days left in a year
for ((*month) = 0; (*month) < 12; (*month)++) {
if ((*month) == 1) {
if (LEAP_YEAR(*year)) {
if (tempDay - 29 < 0) {
break;
} else {
tempDay -= 29;
}
} else {
if (tempDay - 28 < 0) {
break;
} else {
tempDay -= 28;
}
}
} else {
if (tempDay - monthDays[(*month)] < 0) {
break;
} else {
tempDay -= monthDays[(*month)];
}
}
}
(*month)++;
*day = tempDay+2; // one for base 1, one for current day
}
void initializeWiFi() {
while (status != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to SSID: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
// Connect to WPA/WPA2 network. Change this line if using open or WEP network:
status = WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
// status = WiFi.begin(ssid);
// wait 10 seconds for connection:
delay(10000);
}
Serial.print("Success to connect AP:") ;
Serial.print(ssid) ;
Serial.print("\n") ;
// local port to listen for UDP packets
Udp.begin(2390);
}
void printWifiData()
{
// print your WiFi shield's IP address:
Meip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(Meip);
Serial.print("\n");
// print your MAC address:
byte mac[6];
WiFi.macAddress(mac);
Serial.print("MAC address: ");
Serial.print(mac[5], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[4], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[3], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[2], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[1], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(mac[0], HEX);
// print your subnet mask:
Mesubnet = WiFi.subnetMask();
Serial.print("NetMask: ");
Serial.println(Mesubnet);
// print your gateway address:
Megateway = WiFi.gatewayIP();
Serial.print("Gateway: ");
Serial.println(Megateway);
}
如下圖所示,讀者可以看到本次實驗-網路校時測試程式結果畫面。
透過網路校時設計RTC時鐘模組
整合上述程式,我們可以將RTC時鐘模組的網路校時功能給予實作出來。打開Ameba開發工具「Sketch IDE」整合開發軟體撰寫一段程式,如下表所示之網路校時RTC時鐘模組測試程式,就可以透過Ameba WiFi模組取得網路時間並校正時鐘模組。
網路校時RTC 時鐘模組測試程式(SetTime_fromNet)
#include
#include "RTClib.h"
RTC_DS1307 RTC;
// above is used for RTC
#include "PMType.h"
#include
#include
#include
// Aboev is used for WIFI
uint8_t MacData[6];
char ssid[] = "linkitone"; // your network SSID (name)
char pass[] = ""; // your network password
char server[] = "gpssensor.ddns.net"; // the MQTT server of LASS
#define MAX_CLIENT_ID_LEN 10
#define MAX_TOPIC_LEN 50
char clientId[MAX_CLIENT_ID_LEN];
char outTopic[MAX_TOPIC_LEN];
IPAddress Meip , Megateway , Mesubnet ;
String MacAddress ;
int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS;
WiFiUDP Udp;
const char ntpServer[] = "pool.ntp.org";
const long timeZoneOffset = 28800L;
const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time stamp is in the first 48 bytes of the message
const byte nptSendPacket[ NTP_PACKET_SIZE] = {
0xE3, 0x00, 0x06, 0xEC, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x31, 0x4E, 0x31, 0x34,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
};
byte ntpRecvBuffer[ NTP_PACKET_SIZE ];
#define LEAP_YEAR(Y) ( ((1970+Y)>0) && !((1970+Y)%4) && ( ((1970+Y)%100) || !((1970+Y)%400) ) )
static const uint8_t monthDays[] = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; // API starts months from 1, this array starts from 0
uint32_t epochSystem = 0; // timestamp of system boot up
unsigned long epoch ;
int NDPyear, NDPmonth, NDPday, NDPhour, NDPminute, NDPsecond;
// this is used for WIFI and NTP
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
initRTC() ;
// init RTC Modules
MacAddress = GetWifiMac() ;
ShowMac() ;
initializeWiFi();
ShowNTPDateTime() ;
SetRTCTime(NDPyear, NDPmonth, NDPday, NDPhour, NDPminute, NDPsecond);
delay(1500);
}
void loop() { // run over and over
delay(1000); // delay 1 minute for next measurement
Serial.print("Now RTC Data and Time is :") ;
Serial.print(ShowDateTime()) ;
Serial.print("\n") ;
delay(1000) ;
}
void ShowNTPDateTime()
{
retrieveNtpTime() ;
getCurrentTime(epoch + timeZoneOffset, &NDPyear, &NDPmonth, &NDPday, &NDPhour, &NDPminute, &NDPsecond);
//ttt->year = NDPyear ;
Serial.print("NDP Date is :");
Serial.print(StringDate(NDPyear, NDPmonth, NDPday));
Serial.print("and ");
Serial.print("NDP Time is :");
Serial.print(StringTime(NDPhour, NDPminute, NDPsecond));
Serial.print("\n");
}
void ShowMac()
{
Serial.print("MAC:");
Serial.print(MacAddress);
Serial.print("\n");
}
void ShowInternetStatus()
{
if (WiFi.status())
{
Meip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print("Get IP is:");
Serial.print(Meip);
Serial.print("\n");
}
else
{
Serial.print("DisConnected:");
Serial.print("\n");
}
}
void initRTC()
{
Wire.begin();
RTC.begin();
if (! RTC.isrunning()) {
Serial.println("RTC is NOT running!");
}
}
String ShowDateTime()
{
return StrDate() + " " + StrTime() ;
}
String StrDate() {
String ttt ;
//nowT = now;
DateTime now = RTC.now();
ttt = print4digits(now.year()) + "-" + print2digits(now.month()) + "-" + print2digits(now.day()) ;
//ttt = print4digits(NDPyear) + "/" + print2digits(NDPmonth) + "/" + print2digits(NDPday) ;
return ttt ;
}
String StringDate(int yyy, int mmm, int ddd) {
String ttt ;
//nowT = now;
ttt = print4digits(yyy) + "-" + print2digits(mmm) + "-" + print2digits(ddd) ;
return ttt ;
}
String StrTime() {
String ttt ;
// nowT = RTC.now();
DateTime now = RTC.now();
ttt = print2digits(now.hour()) + ":" + print2digits(now.minute()) + ":" + print2digits(now.second()) ;
// ttt = print2digits(NDPhour) + ":" + print2digits(NDPminute) + ":" + print2digits(NDPsecond) ;
return ttt ;
}
String StringTime(int hhh, int mmm, int sss) {
String ttt ;
ttt = print2digits(hhh) + ":" + print2digits(mmm) + ":" + print2digits(sss) ;
return ttt ;
}
String print2digits(int number) {
String ttt ;
if (number >= 0 && number < 10) { ttt = String("0") + String(number); } else { ttt = String(number); } return ttt ; } String print4digits(int number) { String ttt ; ttt = String(number); return ttt ; } String GetWifiMac() { String tt ; String t1, t2, t3, t4, t5, t6 ; WiFi.status(); //this method must be used for get MAC WiFi.macAddress(MacData); Serial.print("Mac:"); Serial.print(MacData[0], HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[1], HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[2], HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[3], HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[4], HEX) ; Serial.print("/"); Serial.print(MacData[5], HEX) ; Serial.print("~"); t1 = print2HEX((int)MacData[0]); t2 = print2HEX((int)MacData[1]); t3 = print2HEX((int)MacData[2]); t4 = print2HEX((int)MacData[3]); t5 = print2HEX((int)MacData[4]); t6 = print2HEX((int)MacData[5]); tt = (t1 + t2 + t3 + t4 + t5 + t6) ; Serial.print(tt); Serial.print("\n"); return tt ; } String print2HEX(int number) { String ttt ; if (number >= 0 && number < 16)
{
ttt = String("0") + String(number, HEX);
}
else
{
ttt = String(number, HEX);
}
return ttt ;
}
// send an NTP request to the time server at the given address
void retrieveNtpTime() {
Serial.println("Send NTP packet");
Udp.beginPacket(ntpServer, 123); //NTP requests are to port 123
Udp.write(nptSendPacket, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
Udp.endPacket();
if (Udp.parsePacket()) {
Serial.println("NTP packet received");
Udp.read(ntpRecvBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read the packet into the buffer
unsigned long highWord = word(ntpRecvBuffer[40], ntpRecvBuffer[41]);
unsigned long lowWord = word(ntpRecvBuffer[42], ntpRecvBuffer[43]);
unsigned long secsSince1900 = highWord << 16 | lowWord; const unsigned long seventyYears = 2208988800UL; // epoch = secsSince1900 - seventyYears + timeZoneOffset ; epoch = secsSince1900 - seventyYears ; epochSystem = epoch - millis() / 1000; } } void SetRTCTime( int yr, int mon, int dd, int hr, int mins, int secs) { RTC.adjust(DateTime(yr, mon, dd, hr, mins, secs)); } void getCurrentTime(unsigned long epoch, int *year, int *month, int *day, int *hour, int *minute, int *second) { int tempDay = 0; *hour = (epoch % 86400L) / 3600; *minute = (epoch % 3600) / 60; *second = epoch % 60; *year = 1970; *month = 0; *day = epoch / 86400; for (*year = 1970; ; (*year)++) { if (tempDay + (LEAP_YEAR(*year) ? 366 : 365) > *day) {
break;
} else {
tempDay += (LEAP_YEAR(*year) ? 366 : 365);
}
}
tempDay = *day - tempDay; // the days left in a year
for ((*month) = 0; (*month) < 12; (*month)++) {
if ((*month) == 1) {
if (LEAP_YEAR(*year)) {
if (tempDay - 29 < 0) {
break;
} else {
tempDay -= 29;
}
} else {
if (tempDay - 28 < 0) {
break;
} else {
tempDay -= 28;
}
}
} else {
if (tempDay - monthDays[(*month)] < 0) {
break;
} else {
tempDay -= monthDays[(*month)];
}
}
}
(*month)++;
*day = tempDay + 2; // one for base 1, one for current day
}
void initializeWiFi() {
while (status != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to SSID: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
// Connect to WPA/WPA2 network. Change this line if using open or WEP network:
// status = WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
status = WiFi.begin(ssid);
// wait 10 seconds for connection:
delay(10000);
}
Serial.print("Success to connect AP:") ;
Serial.print(ssid) ;
Serial.print("\n") ;
// local port to listen for UDP packets
Udp.begin(2390);
}
void printWifiData()
{
// print your WiFi shield's IP address:
Meip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(Meip);
Serial.print("\n");
// print your MAC address:
byte mac[6];
WiFi.macAddress(mac);
Serial.print("MAC address: ");
Serial.print(mac[5], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[4], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[3], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[2], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(mac[1], HEX);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(mac[0], HEX);
// print your subnet mask:
Mesubnet = WiFi.subnetMask();
Serial.print("NetMask: ");
Serial.println(Mesubnet);
// print your gateway address:
Megateway = WiFi.gatewayIP();
Serial.print("Gateway: ");
Serial.println(Megateway);
}
如下圖所示,可以看到本次實驗「網路校時RTC 時鐘模組」測試程式結果畫面,在下圖第一個紅框中,取得網路校時的時間;在第二個紅框中,已將網路校時的時間寫入RTC時鐘模組,之後就由模組讀出時間,不必浪費網路頻寬,為了取得時間資料,不斷向網路校時伺服器要求時間,不僅加快了系統的速度,也省去了網路不必要的頻寬浪費。
小結
本文主要介紹Ameba開發板如何透過WiFi模組連接上網際網路,去取得網路校正時間,並且成功校正RTC時鐘模組。這樣的功能,可以說是網路化、實務化的核心功能,透過解說,相信讀者更可以應用RTC時鐘模組到商業化產品,進而將本技術應用在物聯網的核心技術。
- 【大氣監控站台開發案例(下)】環境監控即時監控看板 - 2021/11/25
- 【大氣監控站台開發案例(中)】環境監控雲端平台系統介紹 - 2021/11/02
- 【大氣監控站台開發案例(上)】 大氣監控站建置實例介紹 - 2021/10/18
訂閱MakerPRO知識充電報
與40000位開發者一同掌握科技創新的技術資訊!







Trackbacks/Pingbacks